Emabond Plastic Welding vs. Mechanical Fasteners: A Comprehensive Comparison
When it comes to joining plastic components, there are several methods available, with plastic welding and mechanical fasteners being among the most popular. Both techniques have their own advantages and drawbacks depending on the application, material, and requirements. This article discusses the advantages that Emabond welding has compared to using mechanical fasteners in a production setting.
What is Emabond Plastic Welding?
Emabond plastic welding is a process that uses electromagnetic induction to weld thermoplastic materials. It involves placement of a susceptor material into the joint area, and an induction coil that generates heat to melt and bond the plastic parts together. This method creates a seamless joint without any need for adhesives, solvents, or additional components. Read More
What are Mechanical Fasteners?
Mechanical fasteners include screws, bolts, nuts, rivets, and other devices that physically hold materials together. This traditional method is widely used across various industries and works by applying pressure to keep components in place. It is suitable for a range of materials including plastics, metals, and composites.

Key Comparison Factors
Below, we compare Emabond plastic welding and mechanical fasteners based on several key factors:
How Strong is Emabond plastic welding?
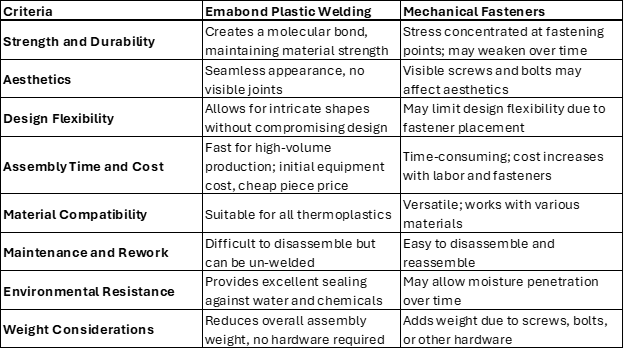
Emabond welding creates a strong molecular bond between plastic parts, resulting in a durable connection that maintains the material’s original strength. This is especially beneficial for applications requiring high load-bearing capacity. In contrast, mechanical fasteners provide reliable strength but can suffer from material fatigue over time, as the stress concentrates around the fastening points, making them susceptible to vibration and thermal cycling.
What does the Emabond Joint design look like compared to fasteners?
Emabond welding offers a seamless appearance, with no visible joints or fasteners, which enhances the aesthetic appeal of finished products. It also allows for more intricate designs without compromising the look. Mechanical fasteners, however, are visible on the exterior of products, which may not be ideal for consumer-facing items. They can also limit design possibilities since extra material may be needed to accommodate fastener placement.
Assembly Time and Cost compared to plastic welding:
While Emabond welding requires an initial investment in specialized equipment, the process is quick and efficient for high-volume production. Once set up, the system can weld multiple parts rapidly, lowering labor costs. On the other hand, mechanical fasteners can be time-consuming to install, especially for assemblies requiring numerous fasteners, which increases labor expenses. Fasteners and gaskets themselves also add to the cost much more than the Emabond’s susceptor material.
Material Compatibility:
Emabond plastic welding is suitable for a wide range of thermoplastics, even some plastics that were thought to be incompatible by more common plastic welding technologies. Mechanical fasteners, by contrast, can join virtually any material, offering greater versatility in multi-material assemblies.
Plastic Welding Maintenance and Rework vs Mechanical Fasteners:
Welded joints created by Emabond are non-permanent, but the weld does make disassembly challenging. If requested, an Emabond weld machine can be used to un-weld the part to harvest any internals of the thermoplastics that might be of higher value to a customer. This practice is commonly used at Emabond for fiberoptic products. Un-welding the product does not make it viable in the future, unfortunately. Mechanical fasteners are much easier to remove and reassemble, facilitating maintenance and rework when needed. If it is common for an assembly to be taken apart for maintenance, customers should stick to using mechanical fasteners for their products.
Environmental Resistance:
Emabond welding seals joints completely, providing excellent resistance to water, chemicals, and other environmental factors. This makes it ideal for applications exposed to harsh conditions. Although mechanical fasteners can be corrosion-resistant, they may still allow moisture to penetrate the joint over time, potentially compromising the assembly. Gaskets that are usually coupled with mechanical fasteners for a leak proof seal also have a shelf life, while Emabond welds do not degrade over time.
By evaluating these factors, you can determine which joining method aligns better with your project requirements. While Emabond welding is ideal for seamless, durable assemblies, mechanical fasteners offer versatility and ease of maintenance, making them suitable for projects requiring frequent adjustments.

