How Emabond Welding Stands Against Ultrasonic Welding for Plastics
Plastic welding is a crucial process in various industries, from automotive to electronics. Among the diverse welding techniques available, Emabond welding and Ultrasonic welding stand out as popular choices for bonding plastics. Both methods offer unique advantages and are suitable for specific applications. This post will provide an in-depth comparison between Emabond welding and Ultrasonic welding, focusing on their principles, advantages, disadvantages, and best-use cases for engineers specializing in plastic welding.
What is Emabond Welding?
Emabond welding is a process that uses electromagnetic energy to generate heat, which bonds plastic materials together. The technique relies on an Emabond susceptor material, a specialized thermoplastic material that acts as a bonding agent between two plastic parts.
- How It Works: Emabond welding involves placing the Emabond adhesive between two plastic parts. An electromagnetic field is then applied to generate heat through induction, causing the adhesive to melt and flow. The molten adhesive fills any gaps between the parts, creating a strong bond as it cools and solidifies.
- Advantages of Emabond Welding:
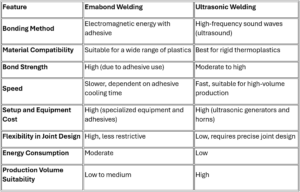
- High Bond Strength: The use of a specialized susceptor materials allows for strong and durable bonds, making it ideal for high-stress applications.
- Versatility in Material: Emabond welding can bond a wide range of plastics, including materials that are challenging to weld using other methods.
- Controlled Heating: The electromagnetic process offers precise heating control, reducing the risk of overheating and material degradation.
- Minimal Surface Preparation: The process requires minimal surface preparation, making it efficient for manufacturing.
- Disadvantages of Emabond Welding:
- Initial Setup Costs: The equipment and material required for Emabond welding can be extra costs added depending on the size and complexity of the part being welded.
- Limited Speed: The welding process can be slower compared to ultrasonic welding.
- Specialized Susceptor Material Required: The need for specific material adds complexity to inventory management and a piece price to the plastic assembly.
- Best Use Cases: Emabond welding is best suited for applications that require strong bonds with a high tolerance for stress and strain. It is commonly used in the automotive and electronics industries for welding parts that need to withstand high temperatures or mechanical stress. Emabond provides many application examples for customers to view.
What is Ultrasonic Welding?
Ultrasonic welding is another widely used technique for joining plastic parts. It uses high-frequency sound waves to generate heat through friction, melting the interface of the parts to create a bond.
- How It Works: In Ultrasonic welding, a horn (sonotrode) delivers ultrasonic vibrations to the plastic parts that are held together under pressure. The frictional heat generated by these vibrations causes the material at the interface to melt and fuse, forming a solid bond once it cools.
- Advantages of Ultrasonic Welding:
- High-Speed Process: Ultrasonic welding is fast and efficient, making it suitable for high-volume production.
- No Need for Additional Materials: Unlike Emabond welding, Ultrasonic welding does not require additional bonding agents, reducing material costs.
- Clean and Precise: The process is clean, as there is no need for solvents or mechanical fasteners. It provides precise control over the welding process.
- Low Energy Consumption: Ultrasonic welding is energy-efficient compared to other welding techniques.
- Disadvantages of Ultrasonic Welding:
- Material Compatibility: The process works best with rigid thermoplastics and may not be suitable for all types of plastics.
- Initial Equipment Costs: The equipment required for Ultrasonic welding, including ultrasonic generators and horns, can be costly.
- Limited Joint Design Flexibility: Ultrasonic welding requires precise joint design for optimal results, limiting flexibility in product design.
- Best Use Cases: Ultrasonic welding is ideal for mass production scenarios where speed is paramount. It is widely used in the medical device, electronics, and consumer goods industries for assembling small to medium-sized plastic components.
Comparison: Emabond Welding vs. Ultrasonic Welding
Choosing the Right Method for Plastic Welding
Choosing between Emabond welding and Ultrasonic welding depends on several factors, including the material being welded, production volume, required bond strength, and specific application requirements.
- Emabond Welding is a suitable choice for applications that demand high bond strength, versatility in material compatibility, and minimal surface preparation. It is often preferred in industries where durability and resistance to environmental factors are crucial, such as automotive, aerospace, and medical, but can be used in any scenario across the plastic industry.
- Ultrasonic Welding, on the other hand, is ideal for high-speed production environments where efficiency and cost-effectiveness are prioritized. It is widely used in the medical device and electronics sectors, where precision and cleanliness are paramount.
Visual Descriptors
To better understand the differences between these two plastic welding methods, consider the following visual representation:
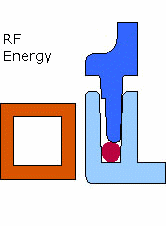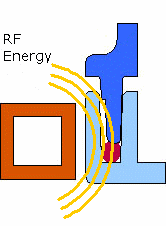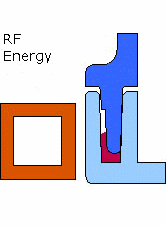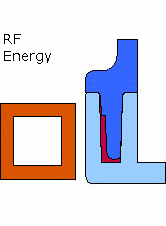
Figure 1: Diagram of Emabond Welding Process Illustration showing the placement of Emabond adhesive, electromagnetic field application, and bonding process.
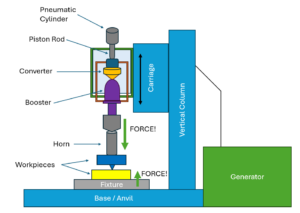
Figure 2: Diagram of Ultrasonic Welding Process Illustration showing the ultrasonic horn, part interface, and bonding process through frictional heat.
Conclusion
Both Emabond welding and Ultrasonic welding offer unique advantages and are suitable for specific plastic welding applications. Understanding the differences in their processes, strengths, and limitations will help engineers make informed decisions about the best welding technique for their needs. While Emabond welding excels in providing strong, durable bonds for a variety of materials, Ultrasonic welding is unmatched in speed and efficiency for high-volume production. The choice ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the application and production environment.
Call to Action: If you need further guidance on selecting the right plastic welding technique or want to explore more advanced welding solutions, contact our team of experts today!