Comparing Emabond Welding to Laser Welding: Which is Best for Your Application?
Welding technologies have evolved significantly over the years, offering a range of solutions for joining materials. Two of the more specialized techniques, Emabond welding and laser welding, cater to different industries and applications. Choosing the right one for your project can enhance efficiency, strength, and precision in your welds. In this article, we’ll compare Emabond welding to laser welding to help you determine which is the better option for your specific needs.
What is Emabond Welding?
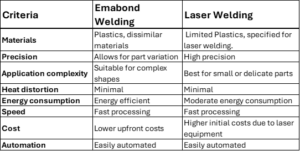
Emabond welding, also known as induction welding, is a process used to weld thermoplastic materials. This method involves applying high-frequency electromagnetic waves to generate heat within the parts to be joined. The heat causes the susceptor material to melt and fuse together the customer parts at the molecular level. Typically used for plastic-to-plastic bonding, Emabond welding is favored for its speed, precision, and ability to bond complex shapes.
Key Benefits of Emabond Welding:
- Strong, uniform bonds: Emabond welding creates reliable and consistent bonds without introducing contaminants.
- Energy efficient: The process focuses energy on the weld area, reducing overall energy consumption.
- No direct contact: Since heating is induced electromagnetically, there’s no need for direct contact with the parts being welded, reducing wear on equipment.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide variety of plastic materials and composites.
- Minimal deformation: The localized heating prevents warping or damaging the material outside the weld area.
What is Laser Welding?
Laser welding uses high-powered lasers to melt material at the weld joint. This precise and clean technique involves directing a laser beam at the interface between two plastic components. The laser targets the lower part, which absorbs the energy and generates heat at the joint, causing the plastic to melt. Pressure is then applied to fuse the materials, forming a strong bond.
Key Benefits of Laser Welding:
- High precision: Ideal for welding delicate or small components, laser welding offers unmatched accuracy and control.
- Fast processing: With minimal heat distortion, laser welding allows for rapid cooling, which speeds up production times.
- Clean welds: Laser welding produces clean, aesthetically pleasing welds without requiring fillers or flux.
- Minimal thermal distortion: The concentrated heat from the laser reduces distortion or damage to surrounding areas, making it ideal for thin materials.
Disadvantages Laser Welding has to Emabond:
- Material Compatibility: Emabond can be used to bond dissimilar materials, and engineered materials. Laser welding is specific to limited plastics with compatible absorption and transmission properties.
- Complex Setup: Laser welding requires precise alignment to the laser, where Emabond specially designs its fixtures to allow for variation in the plastic parts.
- Thickness limitations: The laser can only penetrate a certain thickness of plastic, which makes it less effective for thicker parts.
- Restricted part geometry: Laser welding is not ideal for all shapes as some complex shapes or three dimensional parts may not be suitable for laser welding due to difficulties in focusing the laser. Emabond welding can be performed on highly three-dimensional components.
When to Use Emabond Welding
Emabond welding is ideal if you’re working with thermoplastics or need to bond dissimilar materials or plastic composites. It’s an excellent choice for applications in automotive, consumer products, and appliances where precision is important, but the complexity of shapes makes other welding techniques impractical.
Best industries for Emabond welding:
- Automotive manufacturing
- Consumer electronics
- Packaging
- Industrial equipment
When to Use Laser Welding
Laser welding excels when needing extremely precise, clean welds in delicate components. Its ability to be automated makes it perfect for high-volume production lines that require fast turnaround times with minimal post-processing.
Best industries for laser welding:
- Aerospace
- Medical device manufacturing
- Electronics
- Jewelry and luxury goods
Conclusion: Which Welding Process is Right for You?
Both Emabond and laser welding have distinct advantages and cater to different applications. If your project involves complex plastic parts or requires energy-efficient bonding with minimal thermal distortion, Emabond welding might be the best choice. On the other hand, if your project demands high precision, clean welds, and fast production times, laser welding could be the superior option.
Understanding the needs of your specific application will help you make an informed decision. Whether you’re aiming for cost-efficiency or high precision, the right welding technique can greatly impact the quality and performance of your final product. Contact Emabond to see if our technology is right for your application!

