Emabond Welding vs. Hot Plate Welding: Which is Best for Your Application?
When it comes to plastic welding techniques, Emabond welding and hot plate welding are two popular methods that are often considered for joining thermoplastic parts. Each method offers unique advantages depending on the specific requirements of your application. In this article, we’ll compare these two welding methods to help you make an informed decision.
What is Emabond Welding?
Emabond welding is a process that utilizes electromagnetic energy to heat and bond plastic components. This method of non- contact welding uses an induction coil to create a radio frequency magnetic field, generating heat in a specifically formulated bonding material. The heat generated melts the bonding material, which molecularly joins the plastic parts together.
Advantages of Emabond Welding:
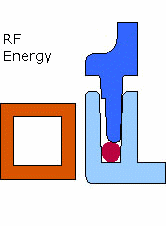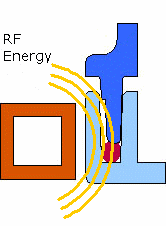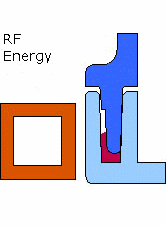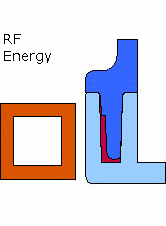
- Precision: Emabond welding allows for highly accurate heating and bonding without directly contacting the part, minimizing the risk of damaging the plastic components.
- Fast Cycle Times: Since it heats only the bonding material, Emabond welding can achieve rapid cycle times, improving efficiency.
- Minimal Stress on Materials: Because heat is localized to the bonding area, the risk of warping or damaging the rest of the component is low.
- Complex Shapes: Emabond welding is ideal for joining irregular or complex shapes, making it a versatile choice.
- Pre-engagement: Emabond joint design allows for parts to be pre-aligned together in the fixture. This takes away any concerns about warp or any other affects result bad parts from other plastic welding techniques.
Disadvantages of Emabond Welding:
- Material Cost: Emabond welding uses its susceptor material as a piece price for the welding process along with the capital RF equipment required for the welding process.
What is Hot Plate Welding?
Hot plate welding, on the other hand, uses direct contact with a heated plate to melt the surfaces of two thermoplastic parts. Once the parts are molten, the heated plate is removed, and the parts are pressed together, creating a bond as they cool.
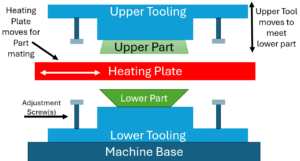
Advantages of Hot Plate Welding:
- Well Known Technology: Hot plate welding is known very well throughout the plastic industry and commonly used in a variety of applications.
- Versatility: Hot plate welding can be used with a wide variety of thermoplastic materials, making it highly adaptable to different industries.
- Large Part Compatibility: This method is suitable for larger plastic parts that require strong, consistent bonds over broad surfaces.
Disadvantages of Hot Plate Welding:
- Longer Cycle Times: Hot plate welding typically requires longer cycle times because it heats the entire surface of the plastic parts.
- Heat-Related Warping/ Flash: There’s a higher risk of warping or deforming the plastic components due to the broader application of heat. Hot plate welding also generates a large amount of flash on the part when welded.
- Equipment Cost: The capital equipment cost of hot plate welding can significantly increase past a standard hot plate application, making the initial investment much greater.
- Safety of Operation: Hot plate welding frequently requires an operator to hand load parts into the equipment, inches away from a scorching hot steel plate.
Key Differences Between Emabond Welding and Hot Plate Welding
- Heating Method: Emabond welding uses electromagnetic energy to create heat, while hot plate welding relies on direct thermal contact with a heated surface.
- Precision and Control: Emabond welding offers more precision since the heat is localized, reducing the chance of damaging the plastic. Emabond also offers pre-engagement of parts. In contrast, hot plate welding applies heat over a larger area, which may result in warping if not carefully controlled before the parts come in contact.
- Cycle Time: Emabond welding tends to be faster due to its targeted heating, whereas hot plate welding often takes longer as it heats entire surfaces.
- Material Compatibility: Hot plate welding and Emabond welding are comparatively equal in material compatibility in terms of the types of thermoplastics it can work with.
- Initial Investment: Hot plate systems tend to have higher startup and utility costs, while Emabond welding systems are typically more affordable up front, with the susceptor material adding a piece price to the part.
Which Welding Method Should You Choose?
The choice between Emabond welding and hot plate welding depends largely on the specifics of your project:
- Emabond welding is ideal if you need precision, fast cycle times, or if you are working with complex shapes. It’s particularly useful in high-volume production settings where speed and accuracy are critical.
- Hot plate welding is better suited for larger parts where aesthetics is not a high concern, or if you have more flexibility with cycle times and know the technology already.
Conclusion
Both Plastic Welding methods offer distinct advantages depending on your application’s requirements. Emabond welding excels in precision, speed, and handling complex geometries, whereas hot plate welding is more versatile and cost-effective for larger parts and different thermoplastics.

