Emabond welding has emerged as a game-changing technology in the field of plastic welding, thanks to its ability to weld various thermoplastics and join dissimilar materials with high precision. Central to this capability is the use of a unique component known as susceptor material. This article will explore how Emabond welding works, the role of the susceptor material, and the advantages it offers in joining thermoplastics and dissimilar materials.
What is Emabond Welding?
Emabond welding, also referred to as electromagnetic welding, is a process that uses radio frequency (RF) energy to generate heat for fusing thermoplastic materials. The process is made possible by incorporating a susceptor material, which responds to electromagnetic energy to produce heat. The susceptor is strategically placed at the joint interface in many different fashions, ensuring localized heating and a strong, durable bond.
How the Susceptor Material Works
The susceptor material plays a critical role in Emabond welding. It is typically made from the base thermoplastics resin and materials with magnetic properties that respond to electromagnetic fields. When exposed to RF energy, the susceptor material heats up rapidly due to the absorption of electromagnetic waves. This localized heat melts the thermoplastic materials at the joint interface, allowing them to fuse together seamlessly.
Welding Thermoplastics with Emabond
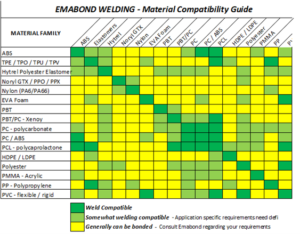
One of the key advantages of Emabond welding is its ability to weld virtually all types of thermoplastics. This includes both amorphous and semi-crystalline polymers, such as:
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
- Nylon (PA)
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
- Elastomers (TPE/TPO,TPU/TPV)
The process is highly adaptable, allowing for fine-tuning to accommodate different melting temperatures and material properties. This versatility makes Emabond welding an ideal choice for industries requiring reliable and robust plastic joints, such as automotive, medical, electronics, and consumer goods.
Joining Dissimilar Materials
Emabond welding stands out in its ability to join dissimilar materials, which is often a challenge with traditional welding methods. This capability is made possible by the susceptor material, which ensures consistent heating and bonding, even when the materials have different melting points or thermal properties. The susceptor material is specifically made for each application to compensate for different properties between parent components.
Placing the susceptor at the joint interface, the process can accommodate varying degrees of thermal conductivity and compatibility between materials, making it possible to join:
- Different types of thermoplastics: For example, bonding polypropylene to TPO, which is difficult using other welding methods.
- Thermoplastics to composites: Enhances the design flexibility for products that incorporate composite materials for added strength and durability.
Advantages of Emabond Welding for Thermoplastics and Dissimilar Materials
- Localized Heating: The susceptor material ensures that heat is generated only at the joint interface, minimizing thermal damage to surrounding areas and preserving the integrity of the materials.
- High Strength and Durability: The welds produced by Emabond are typically stronger and more durable than those achieved with other welding techniques. The process ensures a uniform bond with no voids, reducing the risk of leaks or structural weaknesses.
- Fast Cycle Times: Emabond welding offers rapid cycle times, making it suitable for high-volume production. The process is efficient and can be automated for increased productivity.
- Minimal Part Distortion: Because heat is localized, there is minimal risk of warping or part distortion, which is a common issue in other welding methods.
- Versatility Across Industries: The ability to weld various materials makes Emabond suitable for industries such as automotive, medical devices, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
Applications of Emabond Welding
The versatility of Emabond welding has led to its adoption in various industries. Some key applications include:
- Automotive: Used for bonding fuel tanks, air intake manifolds, and other plastic components that need to withstand high pressures and temperatures.
- Medical Devices: Ideal for creating hermetic seals on medical instruments and devices, ensuring they meet stringent safety and hygiene standards.
- Electronics: Enables the assembly of complex electronic components by bonding plastic housings, connectors, and other parts.
- Aerospace: Used for joining lightweight materials and composites, contributing to weight reduction and fuel efficiency.
Why Choose Emabond Welding?
Emabond welding is a robust, flexible, and efficient welding solution that can handle the challenges of joining thermoplastics and dissimilar materials. Its unique use of susceptor materials allows for precise, localized heating, resulting in high-quality bonds. The advantages of Emabond welding make it a preferred choice for applications requiring strength, durability, and versatility.
Conclusion
Emabond welding is not just another plastic welding technique; it’s a comprehensive solution for joining thermoplastics and dissimilar materials. By leveraging the power of the susceptor material and RF energy, Emabond provides a reliable, efficient, and flexible method for producing strong, high-quality welds across a wide range of industries.
Emabond’s unique capabilities make it an indispensable tool for manufacturers looking to improve product quality and production efficiency. Whether you’re in the automotive, medical, or electronics industry, Emabond welding can provide the reliability and performance you need.